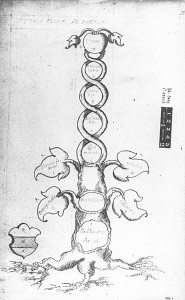
 The axis mundi (also cosmic axis, world axis, world pillar, columna cerului, center of the world), in religion or mythology, is the world center and/or the connection between Heaven and Earth. As the celestial pole and geographic pole, it expresses a point of connection between sky and earth where the four compass directions meet. At this point travel and correspondence is made between higher and lower realms. Communication from lower realms may ascend to higher ones and blessings from higher realms may descend to lower ones and be disseminated to all. The spot functions as the omphalos (navel), the world’s point of beginning.
The axis mundi (also cosmic axis, world axis, world pillar, columna cerului, center of the world), in religion or mythology, is the world center and/or the connection between Heaven and Earth. As the celestial pole and geographic pole, it expresses a point of connection between sky and earth where the four compass directions meet. At this point travel and correspondence is made between higher and lower realms. Communication from lower realms may ascend to higher ones and blessings from higher realms may descend to lower ones and be disseminated to all. The spot functions as the omphalos (navel), the world’s point of beginning.
Because the axis mundi is an idea that unites a number of concrete images, no contradiction exists in regarding multiple spots as “the center of the world”. The symbol can operate in a number of locales at once.
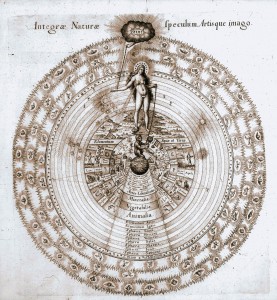 The human body can express the symbol of world axis. Some of the more abstract Tree of Life representations, such as the Sefirot in Kabbalism and in the Chakra system recognized by Hinduism and Buddhism, merge with the concept of the human body as a pillar between heaven and earth. Disciplines such as Yoga and Tai Chi begin from the premise of the human body as axis mundi. The Buddha represents a world centre in human form. Large statues of a meditating figure unite the human figure with the symbolism of temple and tower. Astrology in all its forms assumes a connection between human health and affairs and the orientation of these with celestial bodies. World religions regard the body itself as a temple and prayer as a column uniting earth to heaven.
The human body can express the symbol of world axis. Some of the more abstract Tree of Life representations, such as the Sefirot in Kabbalism and in the Chakra system recognized by Hinduism and Buddhism, merge with the concept of the human body as a pillar between heaven and earth. Disciplines such as Yoga and Tai Chi begin from the premise of the human body as axis mundi. The Buddha represents a world centre in human form. Large statues of a meditating figure unite the human figure with the symbolism of temple and tower. Astrology in all its forms assumes a connection between human health and affairs and the orientation of these with celestial bodies. World religions regard the body itself as a temple and prayer as a column uniting earth to heaven. 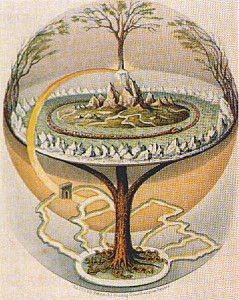 The ancient Colossus of Rhodes combined the role of human figure with those of portal and skyscraper. The image of a human being suspended on a tree or a cross locates the figure at the axis where heaven and earth meet. The Renaissance image known as the Vitruvian Man represented a symbolic and mathematical exploration of the human form as world axis.
The ancient Colossus of Rhodes combined the role of human figure with those of portal and skyscraper. The image of a human being suspended on a tree or a cross locates the figure at the axis where heaven and earth meet. The Renaissance image known as the Vitruvian Man represented a symbolic and mathematical exploration of the human form as world axis.
A common shamanic concept, and a universally told story, is that of the healer traversing the axis mundi to bring back knowledge from the other world.
It is the essence of the journey described in The Divine Comedy by Dante Alighieri. The epic poem relates its hero’s descent and ascent through a series of spiral structures that take him from through the core of the earth, from the depths of Hell to celestial Paradise.
 Anyone or anything suspended on the axis between heaven and earth becomes a repository of potential knowledge. A special status accrues to the thing suspended: a serpent, a victim of crucifixion or hanging, a rod, a fruit, mistletoe. Derivations of this idea find form in the Rod of Asclepius, an emblem of the medical profession, and in the caduceus, an emblem of correspondence and commercial professions. The staff in these emblems represents the axis mundi while the serpents act as guardians of, or guides to, knowledge.
Anyone or anything suspended on the axis between heaven and earth becomes a repository of potential knowledge. A special status accrues to the thing suspended: a serpent, a victim of crucifixion or hanging, a rod, a fruit, mistletoe. Derivations of this idea find form in the Rod of Asclepius, an emblem of the medical profession, and in the caduceus, an emblem of correspondence and commercial professions. The staff in these emblems represents the axis mundi while the serpents act as guardians of, or guides to, knowledge.